
Cloud Security
On-demand delivery of IT resources, i.e. servers, storage, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the Internet (“the cloud”) is known as Cloud computing.
Drive digital business and accelerate value at every stage of your integration and initiative.
Update legacy systems to newer approaches, frameworks and languages.
Services covering full spectrum including readiness assessment, migrations, disaster recovery and performance optimization.
Augment your team clusters on a short or long-term, temporary, and contract-to-hire basis.
We help organizations deliver high-quality software faster.
Improved operations and reduced budgetary expenditures through the reduction of directly-employed staff.
Streamline processes, boosting productivity and reducing manual efforts.
Cutting-edge solutions optimizing infrastructure, ensuring reliability, and enhancing performance.
Enhance efficiency, streamline processes, and drive strategic growth.
Cloud governance is an approved framework that establishes, enforces, and monitors the procedures and policies required as part of the code of conduct for cloud use.
Cloud resource utilization increases over time as more organizations move towards the cloud. Initially, informal guidelines are followed to use cloud resources. Still, as cloud adoption scales across teams with more workloads, there is a need for a proper framework. Cloud governance can help to resolve this issue.
Cloud governance’s objective is to improve data security, control risk, and facilitate the efficient running of cloud systems. The framework is a dynamic document that can evolve with the requirements. It supports other resources and activities that an organization employs.
An organization may have a target operating model (TOM), which serves as a road map for implementing a strategy focused on technology models, success metrics, finance, and procurement. In comparison, the governance structure outlines specific tasks, responsibilities, and rules for each area.
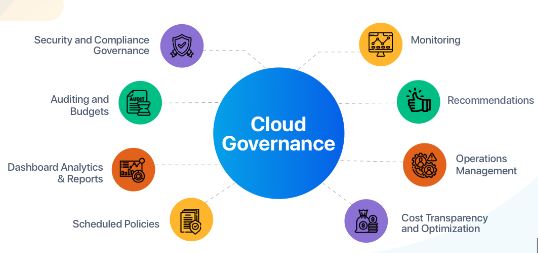
When moving workloads to the cloud, a practical governance approach can help organizations enjoy the full benefits of the cloud and avoid common pitfalls. A cloud management approach must include several important cloud governance components. Organizations consider them necessary for implementing appropriate controls and maximizing the utilization of cloud services. Cloud governance principles include;
The governance framework for security and compliance involves strategies for risk assessment, access management, data encryption, and data security. Other policies under this principle include plans for security thread protection like data leaks and denial-of-service attacks.
Data management is getting more complex as data is growing at a faster rate. Policies for data management include guidelines to manage the data throughout its lifecycle in the organization and on the cloud.
Policies to monitor application performance and infrastructure to ensure the delivery of the expected level of IT services comes under the umbrella of performance management governance.
Framework or strategies to control how cloud resources deliver services are the objectives of operation management governance. SLAs (service-level agreements) is primarily defined and followed to achieve a higher level of smooth operation management.
The major challenge organizations face maintaining cloud infrastructure resources within the confines of their intended deployment. Using IaC (infrastructure as code) can help resolve the challenge. IaC defines what to deploy in the cloud to support the application.
Defining policies to store secrets (credentials and encryption keys) in a centralized repository rather than in scripts or programs comes under configuration governance.
Financial management policies provide a framework for making business decisions about cloud resources. These policies include strategies to control cloud costs. For example, an organization uses managed services and follows SLA strictly to reduce the cost of operational overhead.
Governance is a mix of processes, people, and technologies that drive the cloud journey. Since there is no established model for cloud governance, the organization’s challenge is to modify existing models and incorporate elements of cloud solutions. Organizations can define their cloud governance approach by looking at it through the prisms of people, processes, and technology.
People: Recognize which groups, associations, and people are necessary to define and uphold successful government. These include the executives who must invest in the right resources to guarantee that teams have the authority and know-how to carry out governance duties.
Process: Consider how the business intends to combine technical and non-technical capabilities to establish and enforce activities and guidelines. A strong governance plan needs well-established policies and the ability to assess compliance with procedures using quantitative and valuable indicators.
Technology: The cloud offers technological considerations, including partners and providers who function as company extensions. Enterprises understand how defined governance practices are to be implemented internally and externally.
Organizations can implement a variety of governance techniques. Still, each must consider domains, roles, responsibilities, rules and processes, automation, and governance management. The critical components of a governance framework are explained in the figure below;
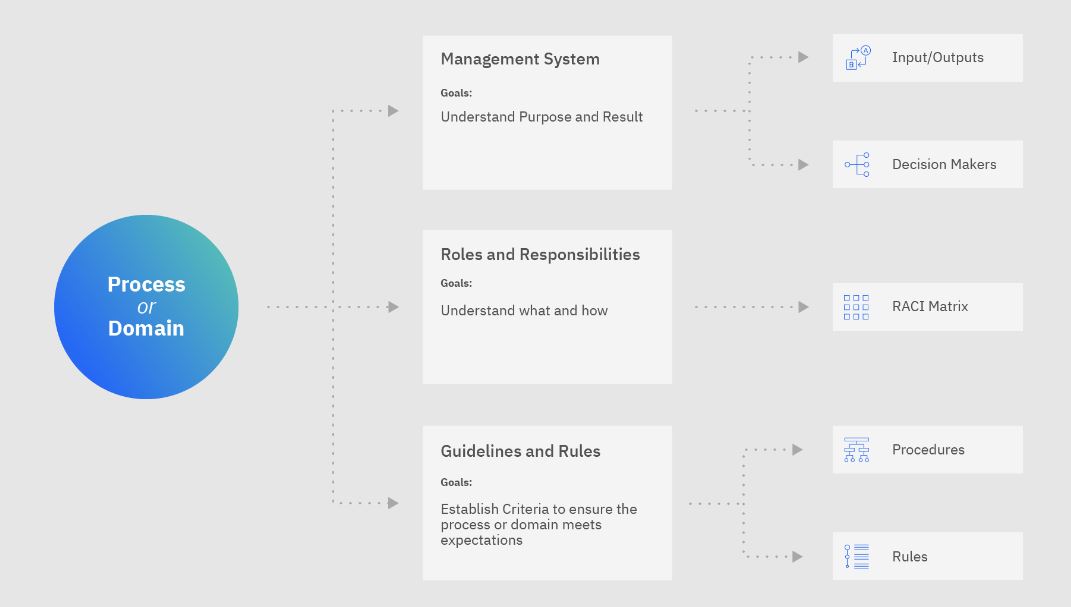
Cloud governance is a continuous process. Organizations must assess if the appropriate policies are still practical after they have been established. As a result, regulations may alter to accommodate new cloud-based technologies. As these issues emerge, the governance architecture needs to change.
Cloud governance Models/Frameworks and standards/Policies are more focused on people and processes rather than specific technologies.
A global standard for corporate IT governance, ISO/IEC 38500 addresses processes, communications, and decision-making. The standard covers establishing roles, supporting IT operations, utilizing technology, making associated acquisitions, keeping track of performance, and adhering to policies.
Businesses can standardize how they choose, provide, and maintain IT services using the ITIL framework, which has comprehensive process descriptions. Companies can also use ITIL to plan strategically for new technological ventures.
The Information Systems Audit and Control Association developed the governance standard COBIT to assist companies and other organizations in managing IT operations. The model includes a framework of processes and practices, process descriptions, control objectives, management guidelines, and maturity models.
Cloud governance must be addressed in a more generalized way. Various organizations will use multiple standard procedures and legal requirements. Organizational frameworks differ, but they always need characteristics like in-scope domains with roles and duties, specific rules and practices, and governance communication and administration.
Arcana provides a comprehensive cloud governance solution by integrating cloud governance and administration into a single platform. In addition to cloud governance, Arcana protects all cloud-based data repositories to assure compliance and maintain the agility and cost savings you obtain from your cloud investments.

On-demand delivery of IT resources, i.e. servers, storage, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the Internet (“the cloud”) is known as Cloud computing.

On-demand delivery of IT resources, i.e. servers, storage, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the Internet (“the cloud”) is known as Cloud computing.